GIT - Version Control
What is GIT?
Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system (DVCS) widely used for tracking changes in software development projects. It allows you to:
- Track Changes: Git keeps a record of all modifications made to your project files over time. This allows you to see how the project evolved, revert to previous versions if needed, and understand who made specific changes.
- Collaboration: Git facilitates teamwork by enabling multiple developers to work on different parts of a project simultaneously. They can then seamlessly merge their changes into a single codebase.
- Offline Development: Unlike some centralized version control systems, Git doesn't require a constant internet connection. Each developer has a complete copy of the project repository, allowing them to work offline and synchronize changes later.
- Branching: Git allows you to create isolated working directories called branches. This is useful for developers to work on new features or bug fixes without affecting the main codebase. Once changes in a branch are ready, they can be merged back into the main project.
Important note;
You'll be familiar with services such as GitHub, or GitLab - these are not Git. These are simply services that offer git-compatible products.
====================================================================================
Installing GIT
apt install git====================================================================================
GIT Usage
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Setting GIT user details
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
git config --global user.name "user.name"Clone/download a GIT repository:
git clone https://github.com/xyzCreate a GIT repository:
(current working directory)
git init Check repository status
git statusPush changes to be committed:
git add .(. being all)
Commit changes:
git commit -m "comment"
View git change logs
git log====================================================================================
Branching
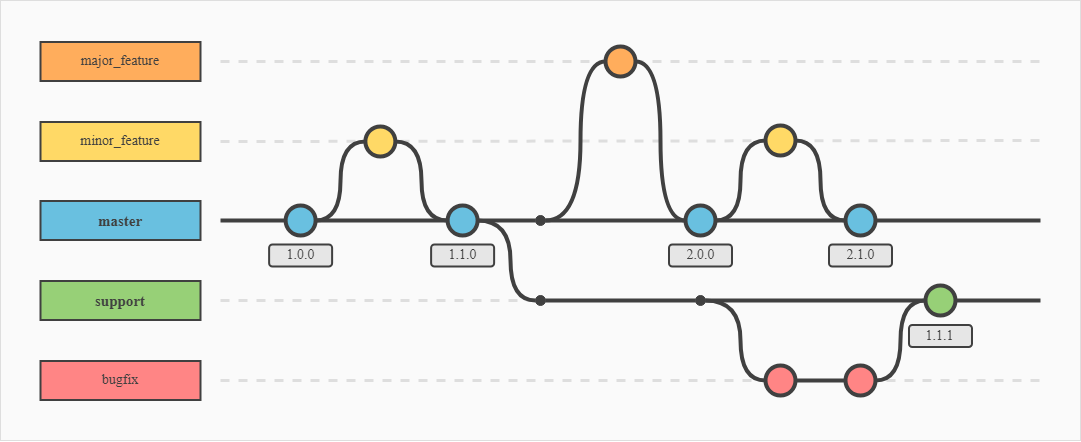
Branching is the term used to describe the usage of multiple Git repositories for development of a single software item.
As you can see above, there is a 'master branch' which would essentially be the release build. The other branches are used for developing and testing features and bug fixes. Once changes have been made, these are committed to the next branch, where they will again need to be committed to the live branch.
Show git branches:
git branchCreate a new branch:
git checkout -b branchnameSwitch branch
git checkout branchnameMerge branches
git merge branchname====================================================================================

No Comments