LVM (Logical Volume Manager)
====================================================================================
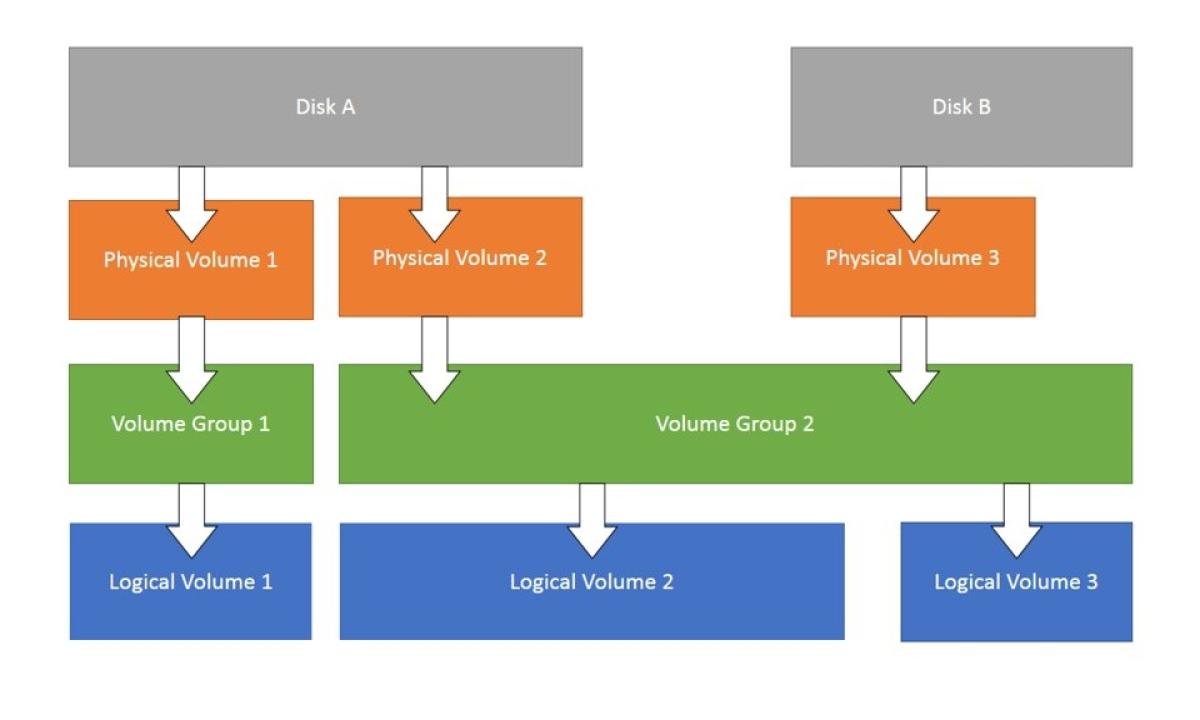
LVM, or Logical Volume Manager, is a tool used on Linux systems to manage disk space in a more flexible way compared to traditional partitioning. It acts like a layer of abstraction between your physical disks and the logical volumes you use for your filesystems. Here's a breakdown of how it works:
Components of LVM:
- Physical Volumes (PV): These are your actual physical hard drives or partitions on those drives. They are the raw storage devices that LVM uses.
- Volume Group (VG): A VG is a collection of PVs that are grouped together under LVM management. You can think of it as a pool of storage space.
- Logical Volume (LV): This is the virtual partition that you create from the storage space in a VG. You can format an LV with a filesystem (like ext4) and use it to store your data just like a regular partition.
Physical Volume (PV) Management:
Initializes a physical disk or partition for use with LVM.
Replace /dev/sdX with the actual device name.
pvcreate /dev/sdXDisplays information about all the PVs in your system.
pvdisplay
Move extents (data chunks) from one PV to another.
This is useful for migrating data or rebalancing PVs within a VG.
pvmove /dev/sdX /dev/sdYResizes a physical disk or partition that's already a PV.
pvresize /dev/sdX
pvremove /dev/sdX: Removes a PV from LVM management.
Volume Group (VG) Management:
vgcreate vg_name /dev/sdX /dev/sdY: Creates a new volume group namedvg_nameusing the specified PVs (/dev/sdXand/dev/sdY). You can add more PVs to a VG later.vgdisplay: Displays information about all the VGs in your system.vgreduce vg_name /dev/sdX: Removes a PV from a volume group (assuming there are other PVs in the VG and the data is not exclusively on the PV being removed).vgremove vg_name: Removes a volume group entirely. This destroys the VG and all its LVs. Use with caution!
Logical Volume (LV) Management:
lvcreate -n lv_name -L <size> vg_name: Creates a new logical volume namedlv_namewith the specified size<size>within the volume groupvg_name. You can specify the size in various units (e.g., M for Megabytes, G for Gigabytes).lvdisplay: Displays information about all the LVs in your system.lvextend -L <size> /dev/mapper/vg_name-lv_name: Extends the size of an existing LV. Replace<size>with the desired expansion size.lvreduce -L <size> /dev/mapper/vg_name-lv_name: Reduces the size of an existing LV. Use with caution as data loss might occur if shrinking beyond the size of the data written on the LV.lvremove /dev/mapper/vg_name-lv_name: Removes a logical volume from the VG. The space becomes available for other LVs within the VG.- lvresize [OPTIONS] LV [PV ...]: Resizes an existing LV. This command was covered in detail previously.
Information and Scanning:
lvmconfig: Displays global LVM configuration information.vgscan: Scans all disks for PVs. This updates LVM's internal information about available physical devices.lvscan: Scans all VGs for LVs. This updates LVM's information about logical volumes within existing VGs.

No Comments