File Permissions and Ownership
====================================================================================
Linux File Permissions
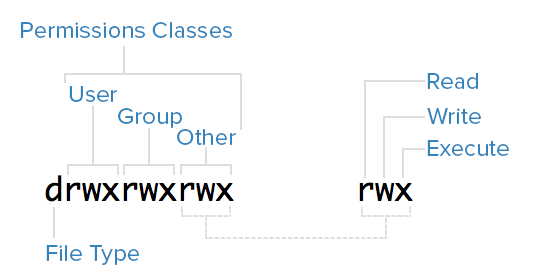
Every file in Linux has permissions, these define which actions can be undertaken by the user,group, and other.
As seen on the file below, permissions are set at the start of the line using 10 characters.
-r--r-xrw- 1 root root 27 May 26 10:56 test.txtThese 10 characters are the permission classes, and are used as follows:
(For file type: - is a file, d is a directory).
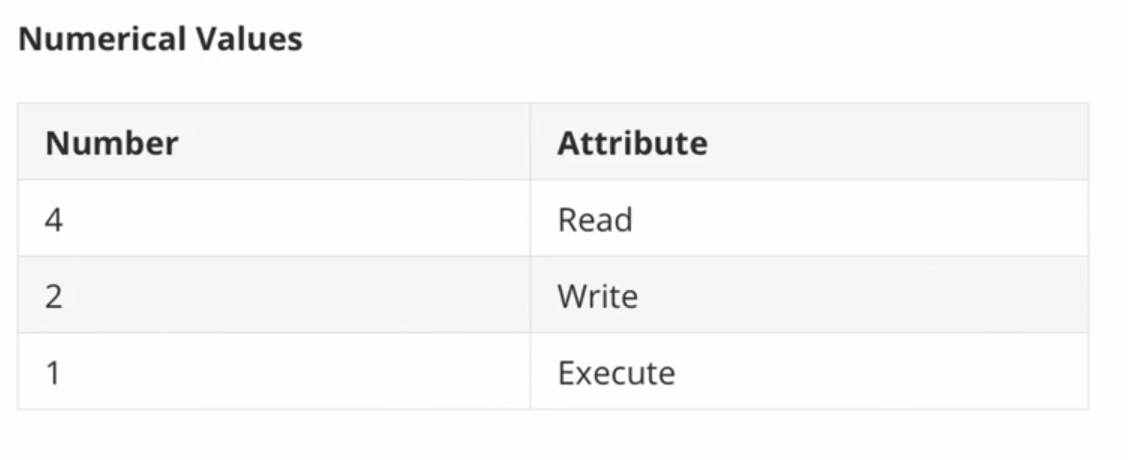
Permissions can also be represented in number format.
Changing Permissions
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Change file/directory permissions (ensure to change permission value)
(Numerical representation)
chmod 777 filename (Letter representation)
chmod u=rwx,g=rwx,o=r====================================================================================
Linux File Ownership
Files in Linux are owned by a user and group.
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 27 May 26 10:56 test.txtChanging user/group
chown newuser:newgroupFor instances where you're wanting to chwon a directory, and all of the subdirectories & files within, we can use the -R (recursive) flag:
chown -R newuser:newgroup directoryname ====================================================================================